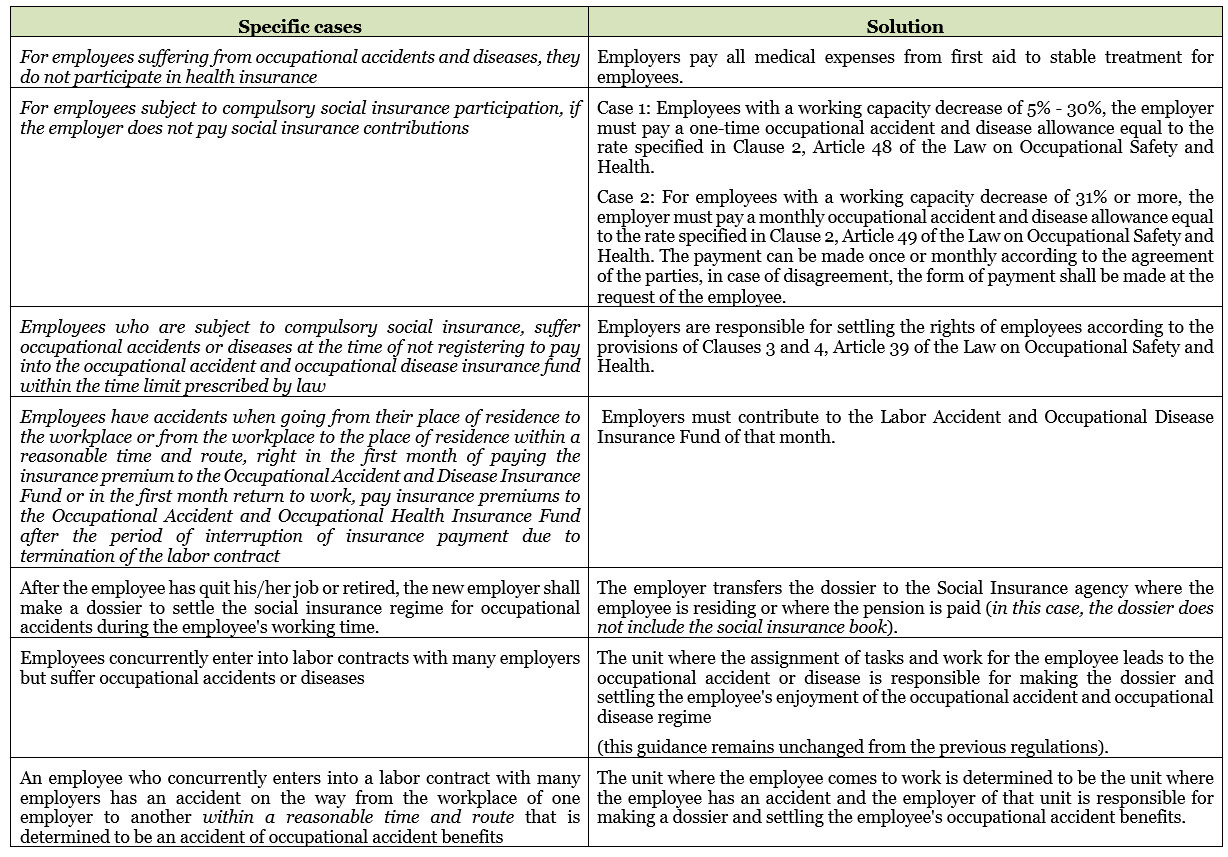
On December 28, 2021, the Minister of Labor, War Invalids, and Social Affairs issued Circular No. 28/2021/TT-BLDTBXH detailing and guiding the implementation of a number of articles of the Law on Occupational Safety and Health benefits for employees suffering from occupational accidents and occupational diseases. This Circular stipulates the responsibility of the employer for employees suffering from occupational accidents and diseases and social insurance regimes for employees suffering from occupational accidents and diseases, applied from March 1, 2022.
Accordingly, one of the highlights in this Circular is the guidance on handling the occupational accident and occupational disease regime for individual cases, specifically as follows:
On January 6, 2022, the Government issued Decree No. 02/2022/ND-CP detailing the implementation of a number of articles of the Law on Real Estate Business. This Decree details the conditions for the transfer of contracts for purchase and sale or lease-purchase of future houses, including the following conditions:
– Having a purchase and sale contract, a lease-purchase contract made according to a form in accordance with the provisions of this Decree; in case the parties have signed the contract before March 1, 2022, the signed contract must be signed;
– Those who have not submitted dossiers to request competent state agencies for issuance of certificates of land use rights and ownership of houses and other land-attached assets;
Contracts for sale, purchase, and lease-purchase of houses must be free of disputes or lawsuits;
– Houses under purchase and sale or lease-purchase contracts are not subject to distraint or mortgage to secure the performance of obligations as prescribed by law unless otherwise agreed by the mortgagee.
– The transfer of house purchase and sale contracts or lease-purchase contracts shall apply to the entire contract. In case of buying, selling, or lease-purchase of many houses in the same contract and the parties wish to transfer each house, the transferor must reach an agreement with the investor to amend the house purchase and sale contract or sign the lease-purchase agreement contract addendum before performing the contract assignment.
Note: Transfering of the future housing purchase and sale contracts does not apply to the social housing purchase and sale, lease-purchase contracts
This Decree takes effect from March 1, 2022.
On January 6, 2022, the Government issued Decree No. 02/2022/ND-CP detailing the implementation of a number of articles of the Law on Real Estate Business. This Decree details the conditions of organizations and individuals trading real estate, including the following conditions:
– Must establish an enterprise in accordance with the law on enterprises or a cooperative in accordance with the law on cooperatives, having a business in real estate;
– Must be publicized on the enterprise’s website, at the headquarters of the Project Management Board (for real estate investment projects), at the real estate trading floor (for business cases) business through the real estate exchange information:
+ Information about the enterprise, including name, head office address, contact phone number, name of the legal representative);
+ Information about real estate put into the business in accordance with the law, including Type of real estate; Real estate location; Information on planning related to real estate; The size of the property; Characteristics, properties, usability, and quality of real estate; information on each type of use purpose and common use area for real estate that is a mixed-use building, apartment building; Actual situation of infrastructure works and services related to real estate; Dossiers and papers on ownership of houses, construction works, land use rights and papers related to real estate investment and construction; guarantee contract, written permission to sell, lease-purchase by a competent state agency for the sale, lease-purchase of houses to be formed in the future;
+ Restrictions on ownership, right to use real estate (if any); Price of the real estate sale, transfer, lease, sublease, lease purchase;
+ Information on the mortgage of houses, construction works, real estate projects put into business (if any);
+ Information on the quantity and type of real estate products being traded, the quantity and type of real estate products sold, transferred, lease-purchased, and the remaining quantity and types of products that are still being traded;
(For the publicly available information specified at this point, which then changes, it must be promptly updated immediately after the change).
+ Only trade in real estate that fully meets the requirements of the Law on Real Estate Business.
In addition, for the investor selected as the investor of a real estate project according to the provisions of law, that investor must have equity (i) not less than 20% of the total investment capital for projects with a land-use scale of fewer than 20 hectares; (ii) not less than 15% of the total investment capital for projects with a land-use scale of 20 hectares or more.
This Decree takes effect from March 1, 2022.
On November 16, 2021, the Government issued Decree No. 102/2021/ND-CP amending Decrees on sanctioning of administrative violations in the field of taxes and invoices; custom; insurance business, lottery business; management and use of public property; practice thrift, fight waste; national reserve; State Treasury; independent accountant. Accordingly, this Decree has amended and supplemented many new regulations on sanctioning of administrative violations in the field of taxes and invoices, including:
1. Increase the statute of limitations for sanctioning administrative violations on invoices: It is 02 years (Previously, the statute of limitations for sanctioning administrative violations on invoices was 01 year).
2. Sanctions for acts of giving and selling goods invoices (except for the act of giving and selling unissued printed invoices and giving and selling ordered printed invoices of customers ordering printed invoices to other organizations and individuals): A fine ranging from VND 20,000,000 to VND 50,000,000 (Previously, this fine was applied to acts of giving and selling purchase invoices from tax authorities but not yet made).
3. The additional sanction for the act of “making invoices without fully stating the required contents on invoices as prescribed”: A fine ranging from VND 4,000,000 to VND 8,000,000;
4. The additional sanction for the act of “losing, burning, damaging invoices that have been made but have not yet declared tax”: The fine level is from VND 4,000,000 to VND 8,000,000;
5. Abolish the regulation on sanctioning administrative violations for the act of “losing, burning or damaging a paid invoice during use or during storage, except for the cases specified in Clauses 1, 2, 3, Article 26 of Decree No.125/2020/ND-CP dated on 19 October 10, 2020, the Government’s regulations on penalties for administrative violations of taxes and invoices are amended and supplemented by Article 1 of Decree No.102/2021/ND-CP”
6. Amendment of regulations on the case that late payment of fines is not charged: During the period of consideration and decision to reduce or exempt fines, the late payment of fines will not be charged (Previously just specified during the period of consideration and decision to exempt fines).
This Decree takes effect from January 1, 2022.
The Law on amendments and supplements to a number of articles of the Law on Handling of Administrative Violations was passed by the XIV National Assembly of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam at its 10th session on November 13, 2020 (hereinafter collectively referred to as an abbreviated as “Amendment Law”).
Through this article, let’s learn with Bizlawyer about new changes in maximum fine levels in fields under the Amendment Law.
Reasons for amendments and supplements
– Firstly: The maximum fine level in some areas of state management has been prescribed since 2012 (the time of promulgation of the Law on Handling of Administrative Violations). At the present time, this fine level is too low compared to socio-economic development.
– Secondly: After nearly 8 years (from the time of promulgation of the Law on Handling of Administrative Violations), a number of violations in the fields of law are increasingly common, sophisticated, and illegal sources of income are: very large, causing great consequences to society, causing economic losses, even affecting the lives and health of people, but the maximum fine applied to these acts is still not commensurate with the nature and extent of the violation, lacks deterrence and is not sufficient to prevent and limit new administrative violations.
– Thirdly: The addition of the maximum fine in Article 24 of the Law on Handling of Administrative Violations for a number of new fields approved by the Standing Committee of the National Assembly stipulates specific maximum fine levels as a legal basis for the Government to stipulate during the implementation of the Law on Handling of Administrative Violations in the past few years are also very important.
– Fourthly: The names of some fields specified in Article 24 of the Law also changed in the laws passed after the Law on Handling of Administrative Violations was promulgated, so they also need to be revised for consistency.
Orientations for amendments and supplements
Firstly: Increase the maximum fine level in some fields;
Secondly: Add the maximum fine for a number of fields not yet specified in Article 24 of the Law on Handling of Administrative Violations;
Thirdly: Modify the names of a number of fields to suit the current Laws promulgated after the Law on Handling of Administrative Violations.
Modified and supplemented content
Increase the maximum fine of 10 fields such as:
– Road traffic: from 40 million to 75 million.
– Prevention and control of social evils: from 40 million to 75 million.
– Essential: from 50 million to 75 million.
– Management and protection of national borders: from 50 million to 75 million.
– Education: from 50 million to 75 million.
– Electricity: from 50 million to 100 million.
– Protecting the interests of consumers: from 100 million to 200 million.
– Irrigation: from 100 million to 250 million.
– Press: from 100 million to 250 million.
– Real estate business: from 150 million to 500 million.
Supplementing regulations on the maximum fine level of 08 fields, such as Foreign Affair; rescue; network security; network information security; state audit; obstructing proceedings; unemployment insurance; print.
Modify the names of some fields such as:
The field of production and trading of livestock and plant varieties into “cultivation”; production and trading of animal feed into “breed”; vocational training into “vocational education”; manage forests and forest products into “forestry”; exploration and exploitation of oil and gas and other minerals into “petroleum activities and other mineral activities”; restricting competition to “competition”; management of irrigation works; protect aquatic resources into “aquatic”.
The above are some new changes in maximum fine levels in fields under the Amendment Law. The Amendment Law will come into force from January 1, 2022.
* This newsletter is only for informational purposes about newly issued legal regulations, not used to advise or apply to specific cases.
Hope the above information is helpful to The Esteemed Readers.
Bizlawyer is pleased to accompany The Esteemed Readers!
The Law on amendments and supplements to a number of articles of the Law on Handling of Administrative Violations was passed by the XIV National Assembly of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam at its 10th session on November 13, 2020 (hereinafter collectively referred to as and abbreviated as “Amendment Law”).
Through this article, let’s learn with Bizlawyer about 04 notable new points of the Amendment Law in the section of general provisions.
Firstly: Clarifying the terms “recidivism” and “repeated administrative violations”
Current Law on Handling of Administrative Violations (Article 2): There is no clear distinction between regulations on “recidivism” and “repeated administrative violations”.
The Amendment Law (Clause 5, Article 2 of the Law on Handling of Administrative Violations) explains the word “recidivism”, according to which: “Recidivism means an individual or organization that has been issued a decision on sanctioning an administrative violation but not yet expires the time limit to be considered not yet sanctioned for an administrative violation but commits an administrative violation that has already been sanctioned. Accordingly, this content is distinguished from the content of “repeated administrative violations” explained in Clause 4, Article 2 of the current Law on Handling of Administrative Violations, Accordingly: “A repeated administrative violation is a case where an individual or organization commits an administrative violation that has previously committed this administrative violation but has not been handled and the time limit for handling has not expired”.
Secondly: Handling repeated administrative violations
The current Law on Handling of Administrative Violations: Point d Clause 1 Article 3 provides that: “A person […] who commits the repeated administrative violations shall be sanctioned for each violation;”. Meanwhile, Point b, Clause 1, Article 10 provides that: “repeated administrative violations is an aggravating circumstance.” Consequences: These regulations have created many difficulties in the process of reviewing and making decisions on sanctioning administrative violations.
The Amendment Law: Added regulations to be more specific on the sanctioning principle for each act in the case of “repeated administrative violations”, specifically: “A person […] who commits the repeated administrative violations shall be sanctioned for each violation, except for cases of repeated administrative violations which are prescribed by the Government as an aggravating circumstance;”. This is expected to remove difficulties in the process of reviewing and making decisions on sanctioning administrative violations.
Thirdly: Time limit for application of administrative handling measures
The Amendment Law has added point dd to Clause 2, Article 6 of the current Law on Handling of Administrative Violations as follows: “dd) Within the time limit specified at Points a, b, c and d of this Clause, if the individual intentionally evades or obstructs the application of administrative handling measures, the time limit shall be recalculated from the time of stop the act of evading, obstructing the application of administrative handling measures”.
This regulation reflects the rigor in the management of the state in the sanctioning of administrative violations in general and the application of administrative handling measures in particular.
Fourthly: Prohibited behaviors
The Amendment Law amends a number of prohibited acts in the handling of administrative violations in Article 12 of the current Law on handling of administrative violations, specifically:
Amending and supplementing Clause 6, Article 12 of the current Law on Handling of Administrative Violations: “6. Identifying improper administrative violations; application of improper and inadequate forms of sanction, sanctioning level and remedial measures to administrative violations.”
Adding Clause 8a after Clause 8, Article 12 of the current Law on Sanctions of Administrative Violations: “8a. Failing to monitor, urge, inspect and organize the enforcement of sanctioning decisions and remedial measures.”
The above amended and supplemented regulations stem from practical needs arising during the implementation process.
Above are 04 notable new points in the Amendment Law.
The Amendment Law will come into force from January 1, 2022.
* This newsletter is only for informational purposes about newly issued legal regulations, not used to advise or apply to specific cases.
Hope the above information is helpful to The Esteemed Readers.
Bizlawyer is pleased to accompany The Esteemed Readers!
The Law on amendments and supplements to a number of articles of the Law on Handling of Administrative Violations was passed by the XIV National Assembly of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam at its 10th session on November 13, 2020 (hereinafter collectively referred to as an abbreviated as “Amendment Law”).
Through this article, let’s learn with Bizlawyer about the most basic and general changes of the Amendment Law.
Completing mechanisms, policies, orders, and procedures in the law on handling of administrative violations and minimizing limitations and inadequacies in the provisions of the Law on Handling of Administrative Violations, contributing to ensuring the effectiveness and efficiency of the law enforcement on the handling of administrative violations in practice, ensuring security, order and social safety.
The Amendment Law includes 03 articles, specifically:
– Article 1: Amending and supplementing a number of articles of the Law on Handling of Administrative Violations (there are 75 clauses).
– Article 2: Amending and supplementing Clause 1, Article 163 of the Law on Civil Judgment Execution No. 26/2008/QH12 (amended and supplemented with a number of articles under Law No. 64/2014/QH13 and Law No. 23/2018/QH14).
– Article 3: Effect of implementation.
A total of 66/142 articles have been amended and supplemented compared to the current Law on Handling of Administrative Violations, in which:
– Comprehensively amending and supplementing: 16 articles;
– Technical amendments: 11/142 articles;
– New addition: 04 articles;
– Abolish 03 articles.
The new provisions of The Amendment Law are expected to have the following impacts:
– Firstly: Ensuring publicity, transparency, clarity, creating favorable conditions for people to perceive law observance and functional forces to perform official duties in practice.
– Secondly: Amending, supplementing, and annulling provisions of the Law on Handling of Administrative Violations are no longer relevant.
– Thirdly: Specific regulations, clear sanctions for handling:
+ Contribute actively to the fight and prevention of administrative violations in the new situation, helping individuals and organizations better understand administrative violations, thereby having appropriate behaviors in accordance with the provisions of the law.
+ Overcoming errors in the application of the Law, thereby contributing to limiting complaints and denunciations of individuals and organizations, and creating trust among the people.
+ Improve the effectiveness and efficiency of the management and enforcement of the law on handling administrative violations.
+ Ensure law enforcement handles administrative violations seriously, consistently, accurately, and effectively, fully ensuring human rights, legitimate rights, and interests of individuals and organizations as stipulated in the Constitution determined.
– Fourthly: Building a transparent and objective legal environment, helping businesses feel secure to invest in production and business, contributing to changing the face of the economy in our country.
– Fifthly: Ensuring the implementation of international commitments on human rights, moving towards international standards on human rights in the direction of openness, transparency, fairness, especially regulations on the application of measures to handle administrative violations, regulations related to minors.
In general, The Amendment Law has marked a new development step in building and perfecting the law on handling administrative violations in particular and the Vietnamese legal system in general.
The Amendment Law will take effect from January 1, 2022.
* This newsletter is only for informational purposes about newly issued legal regulations, not used to advise or apply to specific cases.
Hope the above information is helpful to The Esteemed Readers.
Bizlawyer is pleased to accompany The Esteemed Readers!
On December 10, 2021, the Government issued Decree 112/2021/ND-CP detailing several articles and measures to implement the Law on Vietnamese workers going to work abroad under contracts. In this Decree, there are regulations on increasing the deposit level of enterprises providing the service of sending workers to work abroad, specifically:
– The enterprise deposits of VND 2,000,000,000 (Two billion VND) at a bank, a foreign bank branch legally established and operating in Vietnam (the deposit receiving bank).
(According to current regulations, the deposit level is 1,000,000,000 (One billion VND) and service enterprises can only deposit at commercial banks licensed to operate in Vietnam).
– A service enterprise that assigns a branch to perform service activities of sending Vietnamese workers to work abroad under a contract must make an additional deposit of 500,000,000 VND (Five hundred million VND) for each branch that is assigned to do the work. This is a new regulation that is supplemented with the current one.
This Decree takes effect from January 1, 2022.
On December 24, 2021, the Ministry of Health issued Official Letter No. 10943/BYT-MT providing medical guidance on the prevention and control of the COVID-19 for people allowed to enter Vietnam for short-term work (under 14 days). Accordingly, those who are allowed to enter Vietnam to work for a short time will “not have to undergo medical isolation” but must strictly and fully comply with regulations on COVID-19 prevention and control, the scheme, approved plan, no contact with the community, ensuring safety for short-term entry and those in contact, no cross-contamination during work and no infection in the community. In case an immigrant plans to work and operate in many localities, it is necessary to have a clear plan for moving and be approved by the relevant locality specifically as follows:
– A negative test result for SARS-CoV-2 before entry.
– A valid certificate of international health insurance or a commitment to pay the patient’s treatment costs. Inviting units and organizations in case the entry is infected with COVID-19.
– If you have received a full dose of the COVID-19 vaccine or have been infected with SARS-CoV-2, you need to have documents certifying as prescribed.
– Present a certificate of negative SARS-CoV-2 test result.
– Present a certificate of vaccination or certificate of recovery from the COVID-19 (if any).
– Strictly comply with 5K regulations, install and use the medical declaration application (PC-COVID) during your stay in Vietnam.
– To be transported to the place of residence and moved according to the plan, the work plan under regulations.
– Separate accommodation must be arranged for people on entry at the place of residence for convenient monitoring and management.
– Arrange a separate room/area to take samples for SARS-COV-2 testing at the accommodation to collect samples for all people on entry (sampling rooms/area must be arranged separately, convenient for travel; In case it is not possible to arrange a separate room/area, samples can be taken at the guest room on arrival).
– Organization of sampling, testing SARS-COV-2 (RT-PCR technique with/RT-LAMP) at the place of stay for all entry:
+ For cases that have injected enough doses of vaccine or had recovered from COVID-19: (i) staying for less than 3 days: testing once on the first day; (ii) stay for 03 days or more: test 02 times on the first day and the third day.
+ For other cases: test 3 times on the first day, day 3, and day 7.
+ If the test result is positive for SARS-CoV-2, follow the instructions.
In addition, the person entering, the person in close contact with the person on the entry, the organization inviting the person on the entry must meet the requirements for means of transportation, at work, in meetings, and to sign under regulations.
This Decree takes effect from December 24, 2021.